Introduction
Green tea which is high in the catechin EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) has been associated in two meta-analyses with a reduction in body weight and body fat — especially abdominal fat [1,2] and matcha powder is especially high in EGCG.
Catechin Concentration in Matcha
Catechins make up ~30% of green tea’s dry weight and while ordinary brewed green tea contains ~50—100 mg catechins [3], just 1 gram (~1/3 teaspoon) of matcha powder contains 105 mg of catechins of which 61 mg are EGCGs.
A 2009 meta-analysis of 11 green tea catechin studies found that subjects consuming between 270 to 1200 mg green tea catechins / day (1 — 4 tsp of matcha powder per day) lost an average of 1.31 kg (~3 lbs) over 12 weeks [2], but that the effect of green tea catechins on body composition was significant, even when the weight loss between treated and untreated groups is small (~5 lbs in 12 weeks).
Even with as little as a 3 pound weight loss, the total amount of abdominal fat decreased 25 times more with green tea catechin consumption than without it (−7.7 vs. −0.3%) [2] and the total amount of subcutaneous abdominal fat (fat just below the skin on the abdomen) decreased almost 8 times more with green tea catechin consumption than without it (−6.2 vs. 0.8%) [2].
A 2017 meta-analysis found that consuming as little as 100 and 460 mg/day has shown significant effectiveness on body fat and body weight reduction in intervention periods of 12 weeks or more [1].
How do Green Tea Catechins in Matcha Work?
The mechanisms by which green tea catechins reduce body weight and reduce the amount of total body fat and in particular reduce the amount of abdominal fat are still being investigated but it is thought that green tea catechins increase thermogenesis (increased heat production which would result in increased energy expenditure), increase fat oxidation (using body fat as energy), decrease appetite, result in the down-regulation of enzymes involved in liver fat metabolism, and decrease nutrient absorption [2].
Timing of Matcha Catechin Consumption
Green tea catechins such as EGCG found in matcha are absorbed in the intestine and since the presence of food significantly decreases their absorption, green tea catechins are best consumed 1/2 an hour before meals, or 2 hours after meals.
The timing of green tea catechin intake may also affect the absorption and metabolism of glucose. A study by Park et al [4] found that when green tea catechins were given one hour before to a glucose (sugar) load, glucose uptake was inhibited and was also accompanied by an increase in insulin levels.
Effect of Milk Casein on Catechins
It was previously thought that the protein casein found in milk binds green tea catechins, making them unavailable for absorption in the body, however a recent study found that while the antioxidant activity of polyphenols is lowered from 11-27% by the presence of casein, EGCG which is the catechin in matcha is actually increased by the presence of casein [5].
Final Thoughts…
Consuming between 1 — 4 tsp of matcha powder per day (270 to 1200 mg green tea catechins / day) is sufficient to contribute to weight loss of ~3 lbs in 12 weeks (with no other dietary or activity changes) and more significantly decrease body fat composition, especially abdominal fat.
Along with a well-designed meal plan, beverages containing matcha powder may be helpful for those who have already lost significant amounts of weight and who would like to lose remaining fat on their abdomen.
Warning to Pregnant Women
While EGCG has also been found to be similar in its effect to etoposide and doxorubicin, a potent anti-cancer drug used in chemotherapy [6], high intake of polyphenolic compounds during pregnancy is suspected to increase risk of neonatal leukemia. Bioflavonoid supplements (including green tea catechins) should not be used by pregnant women [7].
High Protein to Energy Matcha Drink

High protein low carb matcha meal replacement
This drink is great after a workout, or as a quick high protein, low carb meal replacement when time doesn’t allow for real, whole food. It may be helpful for those who have already lost significant amounts of weight, yet are having difficulty losing residual fat around their abdomen.
Since matcha does contain caffeine, I recommend drinking these before 2 PM in the afternoon so that the caffeine does not interfere with sleep.
Ingredients
- 1 tsp matcha (green tea) powder (1 tsp = 2 gm)
- 1 scoop unflavoured whey isolate powder (25 g protein per scoop)
- 12 cubes ice cubes
- 1 cup (250 ml) fat free Fairlife® milk (low carb, high protein)
- Optional: 1.5 tsp monk fruit / erythritol sweetener
Method
- Place 1 tsp matcha powder in a small stainless steel sieve and gently press through the sieve into a small bowl with the back of a small spoon
- Put the sieved matcha powder into a ceramic or glass bowl (not metal, as the tannins in the tea will react and give the beverage an ”off” metallic taste)
- Whisk 3 tbsps. boiled and cooled water into the matcha powder using a bamboo matcha whisk until the mixture is smooth and frothy
- Add low carb erythritol sweetener, if desired
- Add 1 scoop of unflavoured whey isolate powder
- Stir in 1 cup Fairlife® (low carb, high protein) milk
- Pour mixture over ice cubes
Macros
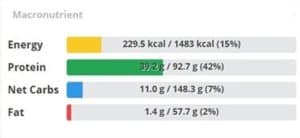
Matcha drink nutritional data from Cronometer
More Info
I design low carb Meal Plans from a variety of perspectives, including a Low Carb High Protein perspective.
Learn about me and the Comprehensive Dietary Package that I offer.
To your good health!
Joy
You can follow me on:
Twitter: https://twitter.com/jyerdile
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/BetterByDesignNutrition/
References
- Vázquez Cisneros LC, López-Uriarte P, López-Espinoza A, et al. Effects of green tea and its epigallocatechin (EGCG) content on body weight and fat mass in humans: a systematic review. Nutr Hosp. 2017;34(3):731-737. doi:10.20960/nh.753 [https://www.nutricionhospitalaria.org/articles/00753/show]
- Hursel R, Viechtbauer W, Westerterp-Plantenga MS. The effects of green tea on weight loss and weight maintenance: a meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009;33(9):956-961. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.135 [https://www.nature.com/articles/ijo2009135]
- Weiss DJ, Anderton CR. Determination of catechins in matcha green tea by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2003;1011(1-2):173-180. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(03)01133-6 [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021967303011336]
- Park JH, Jin JY, Baek WK, et al. Ambivalent role of gallated catechins in glucose tolerance in humans: a novel insight into nonabsorbable gallated catechin-derived inhibitors of glucose absorption. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;60(4):101-109. [http://www.jpp.krakow.pl/journal/archive/12_09/pdf/101_12_09_article.pdf]
- Bourassa P, Côté R, Hutchandani S, et al. The effect of milk alpha-casein on the antioxidant activity of tea polyphenols. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2013;128:43-49. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2013.07.021 [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S101113441300223X]
- Bandele OJ, Osheroff N. Epigallocatechin gallate, a major constituent of green tea, poisons human type II topoisomerases. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008;21(4):936-943. doi:10.1021/tx800010v [https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/tx800010v]
- Paolini M, Sapone A, Valgimigli L. Avoidance of bioflavonoid supplements during pregnancy: a pathway to infant leukemia? Mutat Res. 2003;527(1-2):99-101. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(03)00071-7 [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0027510703000717]

© 2025 BetterByDesign Nutrition Ltd.

Joy is a Registered Dietitian Nutritionist and owner of BetterByDesign Nutrition Ltd. She has a postgraduate degree in Human Nutrition, is a published mental health nutrition researcher, and has been supporting clients’ needs since 2008. Joy is licensed in BC, Alberta, and Ontario, and her areas of expertise range from routine health, chronic disease management, and digestive health to therapeutic diets. Joy is passionate about helping people feel better and believes that Nutrition is BetterByDesign©.
